|
2005 (№1, №2, №3, №4)
2004 (№ 1, №2, №3, №4)
N.V. Kondratyeva
ON A STRUCTURE OF THE PROGRAMMING-METHODICAL MANUAL "THE SELECTION OF SPECIES OF ALGAE OF UKRAINE UNDERGOING PRIOR CONSERVATION"
The draft of manual aimed in unification of approaches to selection of species of algae for Red Data Book of Ukraine is proposed. Description of its chapters is presented. Author recommends supplementing main text of manual by a number of appendixes. The necessity of preliminary discussion of manual structure by experts is stressed, as well as periodical republication of it.
Yu.A. Reunova, N.A. Aizdaicher
THE EFFECT OF DETERGENT ON CHLOROPHYLLS CONTENT IN MICROALGA CHROOMONAS SAUNA (WILS.) BUTCH. (CRYPTOPH7TA) AND DYNAMICS OF ITS NUMBER
The effect of household synthetic detergent (HSD) "Tix" on growth and concentration of chlorophyll a in cryptophyte Chroomonas salina (Wils.) Butch, has been studied. It was shown that low concentration of HSD (0.05; 0.1 and 1.0 mg/L) stimulates growth of alga and has no influence on chlorophyll a content in the cells. At concentration 10 mg/L inhibition of growth and fission of cells is recorded, as well as morphological changes and blocking of chlorophyll a synthesis.
A.A. Sivash, S.I. Los, R.N. Fomishina, E.K. Zolotareva
REGULATOR ROLE OF GLUCOSE IN METABOLISM OF SOME REPRESENTATIVES CYANOPHYTA
The effect of glucose on the growth and pigment composition of two cyanophytes, Spirulina platensis (Nordst.) Geifl. and Nostoc linckia (Roth.) Bom. et Flah. has been studied. It was revealed that they are able to conve rs e on mixotrophic growth. The increase of biomass in 2 - 5 times, and the repression of photosynthesis accompanied inclusion of glucose in metabolism of algae. The effect of glucose on pigment composition of studied algae was extremely different: glucose caused sufficient reduction of all pigments in S. platensis, while in N. linckia pigment composition did not reduced, and sometimes it even increased. The lowest pigment content in S. platensis was in the presence of 1% glucose at the 4-th day of growth: phycocyanine and chlorophyll decreased in 2-2.7 times, allophycocyanine and carotenoids in 1.7-2.0 times in comparison with control. It was found that conversion of S. platensis and N. linckia to mixotrophic growth results in excretion of coproporphyrine in the cultural medium. The assumption was made that glucose blocks biosynthetic way of tetrapirroles on coproporphyrinogene level, and light stimulates formation of earlier predecessors — g-aminolevuline acid.
L.I. Riabushko, I.I. Babich, V.I. Riabushko, L.L. Smirnova
SEDIMENTATION OF PHYTOPLANKTON IN KAZACHIA BAY THE BLACK SEA (UKRAINE)
Seasonal dynamics of species composition, number and biomass of phytoplankton has been studied using sediment traps. Traps have been placed at the depth of 4.5 m in Kazachia Bay of the Black Sea during the period of June 1995 to May of 1996 (exposition time 15-20 days). Trap content was investigated in two fractions separately: 1) suspension of sediment on the bottom of the trap; 2) water over the sediment. Totally 131 taxa of microalgae has been found (Bacillariophyta - 95).
N.A. Milchakova
RED ALGAE (RHODOPHYCEAE RABENH.) OF THE BLACK SEA TAXONOMIC COMPOSITION AND DISTRIBUTION
Modem check-list of Ceramiales (Rhodophyceae) of the Black Sea is compiled using original and literary data, results of taxonomic revisions and nomenclature changes. It incorporates 67 species represented by 88 infraspecies taxa. They belong to 27 genera of four families. Fifteen species are new for the Black Sea flora. The highest species diversity of Ceramiales is recorded near Ukrainian (48 species, 57 infraspecies taxa) and Turkish (52 species, 66 infraspecies taxa) coasts. Factors affecting the appearance and distribution of new, previously unknown species in the Black sea basin are discussed.
N.G. Klochkova, T.N. Krupnova
NEW SPECIES OF LAMINARIALES (PHAEOPHYTA) FROM FAR EAST SEAS OF RUSSIA
Genus Tauya and species Tauya hasicrassa Kloczc. et Krupn., the new genus and species of the order Laminariales (Phaeophyta) are described from the N-W shore of the Sea of Okhotsk. Ecology, distribution and location of the species are presented. Authors discuss differences between new taxa and other representatives of laminarian algae, and prove their affiliation with family Laminariaceae. New genus differs from the other genera of laminarians by thickened base of lamina with rows of bullas, banded location of soruses of sporangia and presence of the glandular cells. In Tauysky gulf at a large depth specific habitat has been found where representatives of new species reach 6 m in length and 1.8 m in breadth.
V.P. Gerasimiuk
STENOPTEROBIA CURVULA (W. SM.) KRAM. (BACILLARIOPHYTA), A NEW FOR UKRAINE DIATOM SPECIES FROM RESERVOIRS OF "YELANETSKAYA STEPPE" NATURE RESERVE
In ephemeral water bodies of "Elanetsky Step" Nature Reserve the species of diatom algae, Stenopterobia curvula (W. Sm.) Kram., has been found for the first time for Ukraine. Ukrainian population of this arctic-alpine species differs from those of other geographical locations by shorter frustules.
S.S. Barinova, LA. Medvedeva
ON TECHNIQUE OF QUANTITATIVE ACCOUNT OF MICROPHYTOBENTHOS IN SMALL RIVERS OF RUSSIAN FAR EAST
The technique of quantitative account of microphytobenthos number and biomass using original record ler is described. It was applied for account of multi species complex communities of foothill rivers of Far East. miendations concerning making of original nucrophytobenthos record chamber in the lab are given. Algorithm of calculation of microphytobenthos number and biomass is explained in detail using the facts. The technique adds to original system of sampling and account of algae of the microphytobenthos, solves the problems of equipment and study of regional peculiarities of species composition. Results of the account allow to monitor the dynamics of number and biomass of algae from different divisions in the community through longitudinal profile of the river, and also to calculate structural features of communities of algae of the microphytobenthos in dynamics. Results of the account are presented with special reference to communities of algae of the Frolovka River (Primorsk Region).
№2 (2004)
Yu.I. Posudin, N.P. Massyuk & G.G. Lilitskaya
EFFECT OF ULTRA-VIOLET RADIATION ON PHOTOMOVEMENT OF TWO SPECIES OF DUNALIELLA TEOD.
Experiments on studying the effect of ultra-violet (UV) radiation on photomovement parameters of two species of green alga of the genus Dunaliella Teod., D. salina Teod. and D. viridis Teod., had demonstrated that the velocity of translational movement of both species does not depend on the intensity and wavelength of UV radiation and duration of the irradiation, which is in contrast to phototopotaxis and the relative motility of the cells. This fact testifies to some possible difference in mechanisms governing these parameters of movement (velocity of forward movement on the one hand, and phototopotaxis and relative motility on the other hand) at the cell level. The conversion of positive phototopotaxis of algae into the negative under UV irradiation has been observed for the first time with further inhibition of phototopotaxis induced by increased duration of irradiation. The greatest inhibitory effect on phototopotaxis of algae is provoked by the radiation of 248-334 nm. The maxima of absorption spectra of proteins related to the motor apparatus and photoreceptor system of the alga are probably located here. The effect of UV radiation on photomovement of both species of Dunaliella had a reversible character: photo-orientation of the cells were restored to the control value at each wavelength (except 248 nm) in two hours after stopping of irradiation of 2 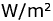 intensity. The dependence of phototopotaxis and motility of the cells of algae on the intensity, wavelength of UV radiation, and duration of irradiation testify to the possibility of using these algae as biotests of natural ultra-violet radiation. intensity. The dependence of phototopotaxis and motility of the cells of algae on the intensity, wavelength of UV radiation, and duration of irradiation testify to the possibility of using these algae as biotests of natural ultra-violet radiation.
N.S. Kuzminova
ASSESSMENT OF TOXIC EFFECTS OF CUPROXAT FUNGICIDE ON PLATYMONAS VIRIDIS ROUCH. (CHLOROPHYTA)
The toxic effects of cuproxat fungicide on the algal culture Platymonas viridis Rouch. (Chlorophyta) were determined. The addition of 0.625; 1.25, and 2.5 mg/L of pesticide into the medium was accompanied by an increase in cell quantity at early growth stages (from 3 to 12 days). The optical density of the culture decreased with the addition of pesticide, as indicated by a fall of cell quantity, and its heat productivity increased at the beginning and at the end of the experiment as compared to the control. The pH of the medium changed insignificantly.
P.R. Makarevich, V.V. Larionov, E.I. Druzhkova
PHYTOPLANKTON DYNAMICS IN ESTUARY AREAS OF NORTHERN SEAS IN THE POLAR NIGHT PERIOD
Data on phytoplankton maintaining a high degree of activity in the polar night period in non-freezing estuaries of the Barents Sea were provided. It was proved that vegetation capacity of autotrophic microalgae during a whole winter season is a distinguishing feature of estuary pelagian ecosystems and it determines their high biological productivity.
Wan Maznah & Mashhor Mansor
PHYCOPERIPHYTON ASSEMBLAGTS IN THE PINANG RIVER BASIN (MALAYSIA)
Epilithic, epipsamic, and epipelic algae were sampled at several locations along the Pinang River Basin. Periphytic algae attached on glass slides were also sampled to determine whether the artificial substrates were collecting representative samples of algal flora naturally present at a site, which were subsequently used in water quality analysis. The relative abundance of certain groups of algae was different on varying substrates. Natural substrates recorded higher densities of algae (947.32 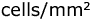 on stones and 1314.36 on stones and 1314.36 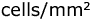 on sediment). Comparative studies of the algal communities on different types of substrates are complicated. The mutual resemblances between artificial and natural substrates were 78.3% (stones and sands) and 78.1% (sediment). Although the substrate type influenced the algal composition, the occurrence of certain species in the Pinang River Basin was also determined by water quality. Glass slides as artificial substrate were useful to compare algal composition between sites with different levels of pollution and to reduce the heterogeneity of naturally occurring substrates, so that the difference in algal composition is due to water quality. on sediment). Comparative studies of the algal communities on different types of substrates are complicated. The mutual resemblances between artificial and natural substrates were 78.3% (stones and sands) and 78.1% (sediment). Although the substrate type influenced the algal composition, the occurrence of certain species in the Pinang River Basin was also determined by water quality. Glass slides as artificial substrate were useful to compare algal composition between sites with different levels of pollution and to reduce the heterogeneity of naturally occurring substrates, so that the difference in algal composition is due to water quality.
F.B. Shkundina
ECOLOGICAL GROUPS OF PHYTOPLANKTON OF BELAYA RIVER (RUSSIA)
The problem of determination of the main ecological groups of river phytoplankton are discussed. In some cases they are determined by complex gradients. Induces of the niche width are used. The attempt was done to compose gradient of species inside ecological groups according to chemical factors of Belaya River using canonical ordination. The spectrum of species according to concentration of ammonium nitrogen was obtained.
N.K. Revkov, E.L. Nevrova
STUDY OF PECULIARITIES OF TAXOCENE STRUCTURE OF BENTHIC BACILLARIOPHYTA USING METHODS OF MULTIVARIATE STATYSTICS (LASPI BAY, THE BLACK SEA, UKRAINE)
Analysis of the structure of communities of benthic diatoms of Laspi Bay (the Black Sea, Crimea) has been done using methods of multivariate statystics. Two complexes of diatoms has been separated in taxocene: Navicula ramosissima Ag. + Licmophora gracilis (Ehr.) Grun. + Grammatophora marina (Lyngb.) Kutz. (complex I) and Tabularia tabulata (Ag.) Snoeijs (complex II). First complex is peculiar to the basic rocks of littoral zone (depth 0.5 m), the second is located at the depth over 3 m and consists of the central main body and marginal zone. Species – indicators and discriminators of mentioned complexes are identified. It was noted that complexes I and II have no distinct floristic margins, and stations located at similar depths but different types of substrates are floristically similar. Relative disposition and shape of domination-diversity curves of mentioned complexes of Laspi Bay reflect gradient of lowering of stress conditions of the habitat in direction: complex I – marginal zone of complex II – main body of complex II.
G.M. Palamar-Mordvintseva, P.M. Tsarenko
CHARALES OF VOLYN POLISSYA, UKRAINE
Generalized data on Charales of Volyn Polissya (forest zone) are presented. Fourteen species of Charales are cited for this region, among them 11 species belong to genus Chara, 2 species – to Nitella, and 1 – to Nitellopsis. Chara fragifera Durien is first cited for Ukraine, record of Chara hispida L. is confirmed for territory of Volyn Polissya (after 1830).
G.G. Lilitskaya
GREEN FLAGELLATE ALGAE OF SMALL WATER BODIES OF KYIV CITY AND KYIV'S ENVIRONS. 1. PRASINOPHYCEAE, CHLOROPHYCEAE (DUNALIELLALES)
As a result of research of the algal flora of Kyiv's small water bodies in 1994-2002 77 species of green flagellate algae which belong to 3 klasses, 8 orders, 13 families and 26 genera were found. Data about 7 species of Prasinophyceae and Chlorophyceae (Dunaliellales) are presented in the publication. One species is new for Ukrainian flora, 4 species are rare. The dеscriptions of morphological peculiarities of Kyiv's populations and original pictures of the taxa are presented.
O.A. Petlovanniy
CHLOROPHYTA OF UKRAINIAN STEPPE NATURE RESERVE. KHOMUTOVSKAYA STEP SITE
First data on species composition of green algae of the Khomutovskaya step site in Ukrainian Steppe Nature Reserve are present. Author, have found 45 species (46 infraspecies taxa) of Chlorophyta from 27 genera, 18 families, 12 orders and 6 classes. All listed taxa are fist sited in Khomutovskaya step site. One species and one infraspecies taxon (Cosmarium pseudarctoum Nordst. in Wittr. et Nordst., Desmodesmus armatus (Chod.) Hegew. var. subalternans (G.M. Sm.) Hegew.) are first sited in Ukraine, 5 species are new for Steppe zone of Ukraine. Taxonomic structure of the chlorophytes from aquatic biotopes of the Khomutovskaya step site and peculiarities of their ecology are revealed.
A.F. Krakhmalny, S.P. Wasser, E.Nevo, A.S. Boltovskoy, S.S. Barinova, M.A. Krakhmalny
NEW FORM OF DINOPHYTA FROM FRESH WATERS OF NORTH ISRAEL
New form of Dinophytes Peridinium volzii Lemm., P. volzii var. volzii f. complexum Krachmalny has been found in water bodies of North Israel. It differs from the type form by bifurcated apical plate. Results of comparative analysis and TEM studies of P. volzii var. volzii f. volzii and P. volzii var. volzii f. complexum morphology, their figures and microphotographs are presented.
K. Popa, A. Cecal, D.I. Kucureanu, G. Nemtsoi, D. Simon, V.F. Rudic, L.E. Cepoi & A.P. Gulea
REMOVAL OF  IONS USING SPIRULINA PLATENSIS (NORDST.) GEITL. AS A BIOPURIFIER IONS USING SPIRULINA PLATENSIS (NORDST.) GEITL. AS A BIOPURIFIER
The methods of radiochemistry, cyclic voltammetry and electron scanning microscopy were employed in experiments with Spirulina platensis (Nordst.) Geitl. CALU-835 to determine chemical and biochemical mechanisms of biological purification of waters containing U(VI). It has been established that under the absence of ionic competition, the S. platensis culture is able to accumulate up to 90% of  ions, which are present in the solution of ions, which are present in the solution of 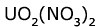 · ·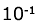 M. The data obtained indicate the formation of large polymer conglomerates, which are connected with the external side of the cell membrane and uranyl, introduced into the system. M. The data obtained indicate the formation of large polymer conglomerates, which are connected with the external side of the cell membrane and uranyl, introduced into the system.
№3 (2004)
А.F. Popova, T.V. Parshikova & R. Kemp
STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL INDICES OF ALGAE CELLS (CHLAMYDOMONAS REINHARDTII DANG.) UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF CATAMINE
The influence of cationic surfactants – catamine (benzalkonium chloride) on the structural changes of the unicellular green algae Chlamydomonas reinchardtii Dang. and their physiological-biochemical indices with using an electron microscopic method were investigated. The decrease in cell number and an increase of its volume as a result of biomembrane reorganization and strengthening of their penetrability for water were established. The significant destructive changes in chloroplast membranes, in particular, the glueing of photosynthetic membranes, the widening of intramembrane space, and also the swelling of plastids, progressive cell vacuolization, and other changes of cell organelles were simultaneously registered, which frequently caused the degeneration of algae cells.
Mamta Awasthi & Debanghshu Narayan Das
HEAVY METAL TOXICITY ON NITRATE REDUCTASE ACTIVITY OF FREE AND IMMOBILIZED ALGAL CELLS
Nitrate assimilation is the principal route for plants and algae to acquire inorganic nitrogen. Nitrate reductase is a multi-enzyme complex bound in the cell membrane in both active and inactive forms. Nitrate reductase is the limiting factor when considering the growth and protein production of algae. Heavy metals interacted negatively with the nitrate reductase (NR) enzyme activity of Chlorella vulgaris Beijer. Nickel was found to be more toxic compared to zinc and cadmium. A highly significant increase in NR activity was observed in the immobilized cells over free cells when supplemented with Ni.
I.A. Maltseva
ALGAE FROM SOILS OF THE SEA OF AZOV TERRITORY (THE ZAPOROZHYE REGION, UKRAINE)
The paper deals with the data on species composition, dominants, soil profile distribution by horizons, quantity and biomass of soil algae of halophilic, meadow-steppe and forest phytocenoses of the Sea of Azov seashore. In 53 species of algae are revealed: Cyanophyta - 21, Eustigmatophyta - 2, Xanthophyta -2, Bacillariophyta - 12, Chlorophyta - 15. It has been established on the basis of the coefficient of floristic community that algosynusia of halophilic phytocenoses differ substantially from those of the meadow-steppe and forest phytocenoses.
V. K. Orleanky
LABORATORY BIOMODELS OF SULFURIC ALGAL-BACTERIAL MAT AND RINGS OF SULFUR (KARPOV'S RINGS)
Twointeresting sulfuric formations were studied in hydrothennal fields of the caldera of the Uzon Volcano (Kamchatka): (1) a sulfuric stratified algal-bacterial mat; and (2) horizontal rings of sulfur on the water surface (Karpov's Rings) formed near the growing colonies of blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). These formations are conditioned by the growth of blue-green algae (genera Oscillatoria and Phormidium belonging to the family Oscillatoriaceae) and the pulsating release of sulfur from hydrothermal springs. The biomodels obtained in the laboratory are similar in their morphology to the natural samples.
L.S. Khaibulina, N.V. Sukhanova, R.R. Kabirov, A.I. Solomeshch
SYNTAXONOMY OF COMMUNITIES OF SOIL ALGAE FROM THE SOUTHERN URALS. 1. THE UNION OP AMPHORO-PHORMIDION ALL. NOVA HOC LOCO
The syntaxonomic analysis of soil algae from the Southern Urals is performed by the Braun-Blanquet method. The new Amphoro-Phormidion union, containing 3 associations, 2 subassociations and 1 variant, is distinguished. Communities of the union are distributed in anthropogenically disturbed soil plots which often represent themselves the artificial ground in the territory of cities located in the arid steppe zones. The abundance of filamentous blue-green algae and mobile diatoms which endure well the salting and which dwell on the surface of the compact ground are observed in all communities of the union.
F.P. Tkachenko
THE SPECIES LIST OF SEAWEEDS OF NORTH-WEST PART OF THE BLACK SEA
The general list of seaweeds of benthos of North-West shelf of the Black Sea was represented. It contains 186 species (Chlorophyta - 62, Phaeophyta - 41, Rhodophyta - 81 and Xanthophyta - 2). Phytogeographycal and ecological characteristics was shown for each species and for rare species - category of danger. 9 species of the algae (Chlorophyta - 3, Rhodophyta - 5, Xanthophyta - 1) are new for this area and were founded the first time.
Mustafa Temel
THE PHYTOPLANKTON OF LAKE TERKOS (ISTANBUL , TURKEY)
The phytoplankton community was investigated at two stations during the 16 cruises on Lake Terkos between May 2000 to July 2001. During 2000-2001, a total of 78 phytoplankton taxa was encountered a quantitative samples. 72 taxa from station 1, and 61 taxa from station 2 were identified. Maximum amount of biomass was formed in station 1 by Synedra acus Kutz. and Ceratium furca (Ehr.) Clap. et Lachm., in station 2 the maximum amount was achieved by species S. acus and Synedra ulna (Nitzsch.) Ehr. The phytoplancton biomass was strongly dominated by diatoms (Cyclotella pseudostelligera Hust, S. acus, Navicula gracillis Ehr., Asterionella formosa Hass. and S. ulna Cryptophyceae members (Cryptomonas erosa Ehr. and C. ovata Ehr.). The maximum biomass value was 1091,6 and 361,4 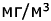 at station 1 and 2 in the Lake Terkos. at station 1 and 2 in the Lake Terkos.
O.S. Tarashchuk
BACILLARIOPHYTA OF THE LOWER STREAM OF THE RIVER SOUTHERN BUG (UKRAINE)
The diatoms of Ihe river Southern Bug, water bodies of its basin and some lakes of Kinburn were investigated during August 2000 and 2001. 93 species of Bacillariophyta, represented by 98 infraspecific taxa, were found. 30 species were shown at first for the river Southern Bug and some water bodies of its basin. The comparison of the received data with literary testifies, that the taxonomic structure of Bacillariophyta is stable enough. The majority of the diatoms of the lower part of Southern Bug and water bodies of its basin make fresh-brackish, brackish-fresh, brackish, mesohalobic and euhalobic species. Among water saprobity indexes prevail a- and p-mesosaprobes. The richest species composition of the diatoms is revealed in phytoepiphyton. Similarity between the diatom lists of species in different biotops is low. The highest degree of floristic similarity have the diatoms of phytoepiphyton and phytobenthos. Species composition of Bacillariophyta of the mouth of the Southern Bug and the nearest water bodies precisely differs from those in the lower part of this river. Distance between stations has the greater value, than type of a water body.
O.A. Sukhow
ABOUT FIRST FOUNDING OT GENUS AMARELLINA MAMET, 1995 (CHLOROPHYTA) IN VISEANS BEDS OF DONETSK BASIN
In Viseans beds of Donetsk basin a green algae derived from the Maghreb (Northern Africa) was found. This algae is of a great interest because it is an earlist founding of representetivs of tribu Bereselleae Maslov et Kulik, 1956.
N.P. Massjuk
ESTIMATION OF TAXONOMIC VALUE OF SOME MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERS OF UNICELLULAR GREEN FLAGELLATED ALGAE (VIRIDIPLANTAE) WITH COMMENTS ON MOLECULAR CLADISTICS
Some morphological characters of unicellular green flagellated algae inherent in their photosynthetic apparatus (plastids number, dimensions, localization, shape, structure of their outside and inside surfaces, pyrenoids presence or absence, pyrenoids number, localization, shape, structure of pyrenoid matrix and starch shirt surrounded it) were observed. In the distribution of diverse states of these characters in different trunks and branches and at various levels of phylogeaetic eukaryotic tree the numerous parallelisms were noted. This phenomenon limits the utilization of these characters in the systematics of higer taxa. Stable and hereditary at the species level these characters are used for identification of species and intraspecific taxa. Utilization of these characters at the superspecific levels stipulates an appearance of heterogeneous taxa, convenient for practice work. Their heterogeneity is confirmed by molecular data. There are no key characters outlining the groups of species within monophyletic clades at the molecular dendrograms. The clades recognized within Chlorophyceae by molecular methods do not correspond to any of the traditional classification systems. So the taxonomic revision of the traditional systems of unicellular green flagellated algae is untimly to-day. In advance it's necessary to realize three preliminary investigating stages at least: 1) to make clear why molecular dendrograms do not correspond to any of the traditional classification system at lower lewel; 2) to work aut the morphologycal-molecular species standart; 3) to find out key characters correlating with genotypic ones.
G.G. Lilitskaya
GREEN FLAGELLATE ALGAE OF SMALL WATER BODIES OF KYIV CITY AND KYIV'S ENVIRONS. 2. CHLAMYDOMONADACEAE (CHLOROPHYCEAE)
As result of research of the algal flora of Kyiv small water bodies in 1994-2001 41 species from family Chlamydomonadaceae that belong to 7 genera were found. 6 species are new for Ukrainian flora: Chlamydomonas cienkowskii Schmidle, Ch. rigensis Skuja, Ch. thiofila H. Etti, Chloromonas serbinowii Wille, Ch. vesterbottnica (Skuja) Gerloff and Vitreochlamys reticulata (L. Peterfi) Massjuk. The descriptions of morphological peculiarities of Kiev populations and original pictures of the taxa are presented.
A.I. Lungu, P. A. Obuh
EUGLENOPHYTA OF THE BASINS OF FILTRATION FIELDS OF WASTEWATER OF THE DROCHIA SUGAR FACTORY (MOLDOVA)
The article generalizes the data on diversity, ecology, and saprobiology of the flora of Euglenophyta in the wastewater treatment system of the Droctua Sugar Factory (DSF). Euglenophyta of the basins of filtration fields are represented by 54 species, and 17 infraspecific taxa belonging to 4 families and 8 genera. Six species and three infraspecific taxa are reported for the first time in Moldova: [Distigma proteus Ehr., Euglenophyta clara Skuja, E. pascheri Swir., Ph. undulatvs (Skv.) Pochm., Trachelomonas bacillifera var. minima Playf., T. conradil Skv., T. hispida var. coronata Lemm., T. hispida var. volicensis Drez., and T. ovata Roll]. Thirty-four taxa are first reported in the flora of the wastewater purification system of DSF. The indicator qualities on the saprobity of the euglenophytic algae (53 species) are shown with the prevailing b-a, b and o-b-mesosaprobe organisms, which is characteristic for the water bodies polluted with organic substances.
№4 (2004)
I.V. Tropin, M.V. Makarov
THE PHOTOSYNTHETIC APPARATUS OF THE BARENTS SEA FUCALES AFTER THE POLAR NIGHT
During the 43 days natural and laboratory experiments it was established that in Ascophyllum nodosum (L.) Le Jol, Fucus vesiculosus L. and F. serratus L. from the Barents Sea the changes in the pigments concentrations take place after polar night. The data obtained are discussed, while taking into account the adaptation of photosynthetic apparatus of algae to the conditions of prolonged low-level illumination, and considering anatomical and morphological differences of their thalli. A suggestion is made on the facultative heterotrophy of littoral Fucales.
V.A. Vasyuk, L.V. Voytenko & L.I. Musatenko
GIBBERELLIN-LIKE SUBSTANCES IN CHARA CONTRARIA A. BR. (CHLOROPHYCEAE)
The research was carried out in the quality and quantity composition of free and conjugated forms of gibberellin-like substances (GLS) in sterile and fertile thallies of the green freshwater alga Chara contraria A. Br. The levels of GLS in oospores, rysoids, two lower internodes were studied in leaves of both middle and apical parts of the fertile thalli of the algae. It was found that the leaves of the upper part of the main stem of the reproductive chara thalli are characterized with high gibberellin content (due mainly to the bound forms).
G.M. Palamar-Mordvintseva, P.M. Tsarenko
RED LIST OF CHARALES OF UKRAINE
The Red List of Сharales of Ukraine is compiled. It includes 35 species of genera Chara (21 species), Lamprotamnium (1), Nitella (10), Nitellopsis (1) and Tolypella (2). One species regards to the first category of protection (endangered to extinction), 10 species – to the second (strongly endangered), 8 – to the third (vulnerable, depleting, endangered), 7 – to category "4" (probably endangered) and 9 – to category "D" (data insufficient). Basic features and characteristics of Charales are analyzed, main categories of threat are described.
G.K. Khursevich, A.V. Kudelsky, S.A. Fedenya, J. Marphy
BACILLARIOPHYTA FROM THE SURFACE LAYER OF BOTTOM SEDIMENTS FROM SMALL UNDRAINED LAKES OF THE SOUTH-EASTERN BELARUS
Bacillariophyta from the surface bottom sediments of six small undrained lakes of the south-eastern Belarus (Tumenskoye, Svyatoye-3, Svyatskoye, Kolpino, Svyatoye-7 and Perstok), contaminated in that or another degree with human impact and Chernobyl-born radionuclides, has been studied for the first time. In the composition of Bacillariophyta have been found 154 species and 29 intraspecific taxa. Studied lakes differing in morphometrical, hydrochemical indexes and the trophic status are characterized by the specific composition of diatoms.
A.F. Krakhmalny, M.V. Tishaeva, Z.A. Panina, M.A. Krakhmalny
A PROBLEM ON IDENTITY OF PROROCENTRUM CORDATUM (OSTENF.) DODGE (DINOPHYTA)
Morphology of Prorocentrum cordatum (Ostenf.) Dodge, the most abundant dinophyte species of the Sea of Azov, has been studied. We focused on general shape and dimensions of cells, structure of periflagellar area, microstructure of valve, arrangement of trichocystian pores and microspines. Morphological variability of species was determined. Comparison of P. cordatum with similar species (Prorocentrum ponticus Krachmalny et Terenko, P. balticum (Lachm.) Loeblich III) was carried out. The problem of identity of P. cordatum and P. minimum (Pavill.) Schiller is discussed. Original LM and SEM photographs illustrate paper.
G.G. Lilitskaya
GREEN FLAGELLATE ALGAE OF SMALL WATER BODIES OF KIEV CITY AND KIEV'S ENVIRONS. 3. CHLOROPHYCEAE: CHLAMYDOMONADALES (PHACOTACEAE) AND VOLVOCALES
As result of research of the algal flora of Kiev small water bodies in 1994-2001 11 species from family Phacotaceae (Chlamydomonadales), that belong to 4 genera, and 11 species from order Volvocales (familis Spondylomoraceae, Tetrabaenaceae, Goniaceae and Volvocaceae), that belong to 6 genera were found. Three species (Coccomonas platyformis Jane, Pteromonas cordiformis Lemm., Gonium formosum Pascher) are new for Ukrainian flora. The descriptions of morphological peculiarities of Kiev populations and original pictures of the taxa are presented.
Je.M. Pankratova, R.Ju. Zyablih, A.A. Kalinin, A.L. Kovina, L.V. Trefilova
CONSTRUCTION OF THE MICROBIAL CULTURE ON THE BASE OF BLUE-GREEN ALGAE NOSTOC PALUDOSUM KUTZ.
Results of investigation confirm a possibility of forming construction of artificial microbial culture on the base of blue-green algae Nostoc paludosum. Compatibility of blue-green algae with Rhizobium leguminosarum, Rh. galegae, Agrobacterium radiobacter, Pseudomonas fluorescens and Azospirillum lipoferum is discussed. We have demonstrated the stability of artificial double and triple mixed cultures and arrangement of the partners in them without Azospirilla. The comparison of treating the seeds of Galegae orientalis by Rh. galegae only with treating by consortia Nostoc paludosum + Rh. galegae showed the significant advantage of the consortia inoculation.
R.R. Kabirov
DEVELOPMENT OF SOIL-ALGOLOGICAL STUDIES IN DEPARTMENT OF BOTANY OF BASHKIR STATE PEDAGOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Results of the 25 years of studies of soil algae carried out in Department of Botany of Bashkir State Pedagogical University are presented. Main achievements and perspectives of development of soil algology in the department are discussed.
№1 (2005)
N.V. Kondratyeva
DEVELOPMENT OF ALGOSOZOLOGICAL STUDIES IN UKRAINE
Paper deals with brief review of the development of sozological studies of algae in Ukraine. They were resulted in appearance of algosozology as the part of phytosozology. Algosozological studies in Ukraine were initiated in 80-90-th of 20 century, and mostly they were carried in autalgosozological direction. Main attention was paid to compilation of various lists of rare species of algae, and also to discussion of methodological approaches to selection of species of algae undergoing top-priority protection, including to Red Lists and Red Data Book of Ukraine. Compilation of methodological manual was begun, and discussion of certain practical problems of algosozology. The nearest future tasks are development of sinalgosozology and algoflorosozology, and the organization of algoreservations for monitoring and conservation of populations and communities of algae.
V.A. Silkin, N.V. Mironova
DYNAMICS OF PRODUCTIONAL AND MORPHOMETRIC INDEXES OF GRACILARIA THALLI IN THE CULTURE
Dynamics of productional and morphometric (diameter, length and number of brunches of all orders) parameters of the thalli of Gracilaria verrucosa (Huds.) Papenf. f. procerrima Esp. has been studied at temperatures 18°, 23° and 27°С, light intensity 30 and 40 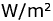 . In 30 days of cultivation the average mass of thallus increased from 0.104 g up to 0.45 g of crude biomass. Maximal values of specific speed of growth of the thalli 0.068 and 0.069 . In 30 days of cultivation the average mass of thallus increased from 0.104 g up to 0.45 g of crude biomass. Maximal values of specific speed of growth of the thalli 0.068 and 0.069 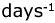 are got at temperatures 18° and 23°C. At 27°C growth processes are substantially slowed. The temperature of environment is a factor determining strategy of morphological organization of thallus. At low temperatures, growth strategy of extensive type is realized through the increase of diameters and length of main axis and branches of 1st and 2nd orders. At the increase of temperature strategy of growth changes on the intensive way, namely, new branches of the second, third and fourth orders are formed. are got at temperatures 18° and 23°C. At 27°C growth processes are substantially slowed. The temperature of environment is a factor determining strategy of morphological organization of thallus. At low temperatures, growth strategy of extensive type is realized through the increase of diameters and length of main axis and branches of 1st and 2nd orders. At the increase of temperature strategy of growth changes on the intensive way, namely, new branches of the second, third and fourth orders are formed.
E.K. Evstigneeva
MORPHOSTRUCTURE OF THE BLACK SEA LAURENCIA (RHODOPHYTA) AND THEIR VARIABILITY
Author investigated external and internal morphostructure of thalli of two agar-containing red algae Laurencia papillosa (Forsk.) Grev. and L. obtusa (Huds.) Lamour. As a result, number of features was revealed: general, species-peculiar, constant, variable. It was found that most of morphometrical and anatomic parameters of laurencia are highly variable depending on age and ecological factors.
E.M. Urmich, H.A. Berdikulov, N.K. Kozyrakhymova
THE CHANGE OF GASEOUS EXCHANGE AND PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIGMENTS OF GREEN ALGA CHLAMYDOMONAS PARIETARIA DILL (Chlorophyta) IN A DAY
In the article the change of the intensity of photosynthesis, respiration and photosynthetic pigments contents in a day of green alga Chlamydomonas parietaria Dill (Chlorophyta) are studied. The intensity of dark respiration in a day is not increased with intensity of photosynthesis. The change of gaseous exchange and photosynthetic pigments in a day are depend on physiology state of cells and biology rhythm.
M. Tavassi, S.S. Barinova, O.V. Anissimova, E. Nevo, S.P. Wasser
ALGAL INDICATORS OF ENVIRONMENT IN THE NAHAL YARGON BASIN, CENTRAL ISRAEL
We recognized 247 species of algae from five divisions in 53 samples of plankton and periphyton collected at 14 stations over the Nahal Yarqon in 2003-2004. Of these, 204 species are indicators of environmental conditions. Species distribution over ecological groups is typical of alkaline freshwater or brackish, temperate, slow-running waters habitable for both planktonic and benthic algae. The indicators of saprobity (Watanabe's scale) show a medium level of organic pollution. The saprobity index S (Sladecek's scale) vary from 1.31 (the upper reaches) to 2.88 near the industrial area of Petakh-Tikva corresponding to II-IV classes of water quality. The self-purification capacity of the Nahal Yarqon ecosystem is rather high corresponding to the olgo- to alphamesosaprobic zones. The environmental pollution index (EPI) varies from 2 to 4 indicating a range of slightly to strongly polluted water of Class II and III. The Water Ecosystem State Index (WESI) testifies to a toxic impact on the algae in the low-water season. The River Pollution Index for saprobity (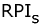 = 2.3), conductivity ( = 2.3), conductivity (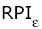 = 2.0-2.7), nitric nitrogen ( = 2.0-2.7), nitric nitrogen (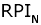 = 1-8), and рН ( = 1-8), and рН (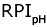 = 7.7-7.8) indicate alkaline moderately mineralized waters with an occasional input of nitrates round the year, corresponding to the Class III water quality and the betamesosaprobic self-purification zone. Our results allow an estimate of self-purification capacity for the Nahal Yarqon on the basis of modern international approaches. We provide indicators for evaluation and monitoring of the river. This study shows the potentials of the algal bioindication method for aquatic ecosystems of Israel. = 7.7-7.8) indicate alkaline moderately mineralized waters with an occasional input of nitrates round the year, corresponding to the Class III water quality and the betamesosaprobic self-purification zone. Our results allow an estimate of self-purification capacity for the Nahal Yarqon on the basis of modern international approaches. We provide indicators for evaluation and monitoring of the river. This study shows the potentials of the algal bioindication method for aquatic ecosystems of Israel.
O.P. Oksiyuk, O.A. Davydov, G.V. Melenchuk
FORMATION OF A SPECIES VARIETY OF THE PHYTOPLANKTON ON THE RIVER SITES OF THE DNIEPER RESERVOIRS
The features of formation of a species variety of the phytoplankton on the river sites of the Dnieper reservoirs under influence of a specific hydrological mode of these sites are considered. On an example of the Kanev reservoir is shown, that the number of kinds on a line of a river site is reduced because of sharp within day of fluctuations of speed of current owing to peak mode of operations hydroelectric power station (HEPS) that settles down above. At the same time initiated by such mode of operations of hydroelectric power station of fluctuation of a level of water promote increase species riches phytoplankton of the basic channel at the expense of receipt of seaweed from water objects of the appendage network. Evenness estimated by an index of a species variety (on Shannon), in phytoplankton of the basic channel and water bodies of the appendage network changed over a wide range depending on number of kinds and degree of their domination.
L.S. Khaibullina, N.V. Sukhanova, R.R. Kabirov, A.I. Solomesch
SINTAXONOMY OF COMMUNITIES OF SOIL ALGAE OF SOUTHERN URAL. 2. UNION KLEBSORMIDIO FLACCIDI-MYRMECION BIATORELLAE ALL. NOVA HOC LOCO
New union Klebsormidio flaccidi-Myrmecion biatorellae is described. It includes algocoenozes of zonal steppe ecosystems on chernozem soils. In floristic composition of algocoenozes of new union dominants are representatives of family Oscillatoriaceae and diatoms from genus Navicula. Another peculiar feature of this union is high diversity of unicellular green and yellow-green algae of X-vital form. Samples were collected in steppe communities located in vicinities or at the territory of settlements which more or less are undergoing recreation. Three new associations and two new subassociations were described. They reflect diversity of communities of new union in Bashkir Ural Region.
N.I. Karayeva, S.K. Jafarova
DIVERSITY OF BACILLARIOPHYTA IN WATER BODIES OF AZERBAIJAN
The brief history of diatoms study of the Azerbaijan water bodies has been presented mainly on the base of the literature data. Compiled list comprised 368 species (408 intraspecific taxa). There are 6 new species (Brachysira vitrea, Karayevia clevei, Navicula phyllepta, Placoneis gastrum, Staurosirella leptostauron, Surirella brebissonii) for the Azerbaijan Republic and 3 new taxa (Sellaphora laevissima, Synedra ulna var. spatulifera, Achnanthes triconfusa) for all the Caucasus among them. The brief data of species diversity in water basins of different geographical regions of Azerbaijan have recorded.
O.S. Gorbulin, D.В. Zarei
YELLOWGREEN ALGAE (XANTHOPHYTA INCL. EUSTIGMATOPHYTA) IN ALGAFLORA OF IRAN
The comparative analysis of the specific structure Xanthophyta, the Iran revealed in water bodies and Ukraine is lead. It is shown, that for florae of both countries coincide individual share Xanthophyta in the general specific variety algaflora, domination of three orders: Mischococcales, Tribonematales, Ophiocytiales, a low relative abundance of the majority of species, finds Xanthophyta in the most typical habitats.
E.N. Demchenko
NEW AND RARE SPECIES OF GREEN FLAGELLATE ALGAE FROM WATER BODIES OF KIEV (UKRAINE)
The results of investigation of morphology of 6 species of green flagellate algae found in small water bodies of Kiev during 2002-2003 are presented. Three species are new records for flora of Ukraine (Monomastix minuta Skuja, Chloromonas plurivacuolata Wawrik, Cephalomonas granulata Higinbotham), three species are rare and interesting finds (Pseudocarteria stellata (Korschikov) H. Ettl, Diplostauron angulosum Korschikov, Hyalogonium fusiforme (Korschikov) H. Ettl). The data about morphology, ecology and geographical distribution of these species are generalized and supplemented. Original drawings and micrographs of species are given.
N.S. Kuzminova, I.I. Rudneva
THE EFFECT OF WASTEWATER ON MARINE ALGAE
Literature review of different wastewater influen се on marine ecosystems is presented. The problems of sewage entering and transformation are broached. Their toxic effect on marine algae are demonstrated. The possibility of biological waste reclamation and using some species of algae culturing in sewage addition for production are discussed.
№2 (2005)
S.I. Genkal
MORPHOLOGICAL VARIABILITY AND TAXONOMY OF DIATOMA TENUE AG. (BACILLARIOPHYTA)
Transmission electron microscopy studies of morphological variability of the valve in populations of Diatoma tenue Ag. have shown that qualitative (valve shape, arrangement of axial area, striae, costae and rimoportula) as well as quantitative (valve lenth and width, number of costae and striae in 10 mm characteristics vary to a great extent. Number of striae in 10 mm and valve width proved to be the most stable and valve length and number of costae in 10 mm -the most labile. It is suggested that D. nanum var. lineare Skabitsch. to be placed in synonym of D. tenue. Based on the literature and our own data a broadened diagnosis of D. tenue is given.
Yu. Posudin, Mitsunobu Kamiya, Akio Murakami, Hiroshi Kawai
EFFECT OF LIGHT OF DIFFERENT INTENSITY ON CHLOROPHYLL FLUORESCENCE OF ULVA PERTUSA KJELLMAN (CHLOROPHYTA)
The effects of high-intensity optical radiation on chlorophyll fluorescence of marine alga Ulva pertusa Kjellman (Chlorophyta) were investigated. Method of pulse amplitude modulated (PAM) chlorophyll fluorescence was used for studying the photoinhibition of photosynthesis of alga. It was shown that the treatment of the dark-adapted samples with low-intensity (30 mmolxm-2xs-1) white light doesn't provide any significant difference between values of optimal quantum yield Yopt of illuminated samples and those samples which were kept in the darkness. The treatment of the samples with high (1800 mmolxm-2xs-1) intensity of white light provokes the photoinhibition: the value of effective quantum yield Yеff decreases up to 33% during 2 hours in comparison with the samples which were kept in darkness. The damage of the photosynthetic apparatus of alga by high irradiances is reversible – after the end of the photoinhibitory treatment the values of fluorescence parameters reached the initial level during the next 2 hours. The possible mechanisms of quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence are discussed. The fluorescence parameters such as effective and optimal quantum yields, photosynthetic efficiency and capacity makes it possible to estimate the effects of high-intensity irradiation on photosynthetic organisms.
E.I. Shnyukova
ACCUMULATION OF METAL IONS BY EXOPOLYSACCHARIDES OF NOSTOC LINCKIA (ROTH) BORN. ET FLACH. (CYANOPHYTA)
This research deals with the accumulation of ions from metals (Cu, Zn, Sr) and Se from the environment by the prokaryotic hormogonic blue-green alga Nostoc linckia (Roth) Born. et Flach. able to actively synthesize exopolysaccharides and also by the preparations of isolated exopolysaccharides. A degree of aquatic environment purification from metal ions depends on the functional state of the culture (age, intensity of proliferation, activity of exopolysaccharide production). Under conditions of culture N. linckia is able to accumulate from 35.82% to 94.16% ions of Cu, Zn, Sr from the environment. Exopolysaccharides play dominating role in the accumulation of the mentioned metals and Se from the environment that is associated with their anionic nature.
S.E. Sadogursky, T.V. Belich
MACROPHYTOBENTHOS IN THE SHORE AQUATIC COMPLEX AT THE CAPE CHAUDA (BLACK SEA, CRIMEA)
Characteristic of the contemporaneous state of macrophytobenthos in the hydrological natural monument Shore Aquatic Complex at the cape Chauda (Black Sea, Crimea) is given. It was registrated 57 species of macrophytes: Magnoliophyta – 2, Charophyta – 2, Xanthophyta – 1, Chlorophyta – 12, Phaeophyta – 9, Rhodophyta – 31. In pseudolittoral was note 22 species, in sublittoral – 53. The facts which were received show the importance of the aquatic complex in the support of ecological balans in this region.
A.B. Zotov
DESCRIPTION OF SPECIFIC SURFACE OF PHYTOPLANKTON TAXONOMIC GROUPS FOR ODESSA REGION (УКРАИНА)
T he specific surface (S/W) p values of a population of 88 of the most mass species of plankton algae, discovered in water bodies in the Odessa coastal zone and related to four groups Bacillariophyta, Dinophyta, Cyanophyta and Chlorophyta are given. The specific surface (S/W) tg values of four groups of inicellular algae and variability of this index during an annual cycle are analyzed.
E.V. Borisova
SPECIES COMPOSITION AND DISTRIBUTION OF CHARALES IN THE UKRAINE
Analysis and generalization of the data available in literature over more than 175 years on the species composition and distribution of algae of the order Charales in water bodies of Ukraine are presented. The revealed species composition (38 species) is rather rich. The natural physiographic zones of the Ukraine in respect to of Charales are investigated non-uniformly, nevertheless their species composition and main regularities of distribution are revealed. Flora of Charales of Ukraine includes 38 species belonging to 5 genera: Chara L. (24), Nitella Ag. (10), Tolypella A. Br. (2), Nitellopsis Hy (1), Lamprothamnium Gr. (1). Among these taxa, 32 species occur in other parts of Europe. Data on distribution of species Chara arcuatofolia Vilh., Ch. dominii Vilh., Ch. fischeri Mig. and Ch. neglecta Hollerb. are given (they were not found in Western Europe).
Faruk Maraslioglu, E. Neyran Soylu&Arif Gonulol
A STUDY ON THE COMPOSITION AND SEASONAL VARIATION OF THE EPILITHIC DIATOMS OF LAKE LADIK (SAMSUN, TURKEY)
The composition and seasonal variations of the epilithic diatoms of Lake Ladik were studied using samples collected from one station between June 2000 and May 2001. Fifty-one taxa were identified belonging to the Bacillariophyta in the epilithon. Aulacoseria distans (Ehr.) Simonsen, Cymbella affinis Kutz., C. prostrata (Berkeley) Cleve, Navicula cryptocephala Kutz., N. halophila, (Grun.) Cleve, N. veneta Kutz. and Surirella linearis W. Smith have become common organisms. Cluster analysis was applied to the epilithic algae community. The seasonal variations of the samples were classified according to their similarity levels. Samples were collected and species richness and diversity (Shannon-Wiener, H) were measured monthly. The results of the analysis supported the results of the counting method. Temperature and light climate that affect the population density were found to be an important factor in explaining the seasonal variation observed in Lake Ladik.
F.P. Tkachenko
THE NEW LOCATION OF RARE SPECIES OF UKRAINE FLORA CHARA UZBEKISTANICA HOLLERB.
The description of new location of rare for Ukraine species of Chara uzbekistanica Hollerb. was represented. This species was founded in the benthos of riverside Danube lakes: Yalpug and Kugurluy.
L.M. Terenko
THE NEW DINOPHYTA OF THE BLACK SEA
The annotation list consists of 28 species and 4 intraspecific taxa of dinoflagellates found in the Odessa Bay of the Black Sea. Is described 24 species and 3 intraspecific of the list are new for the Black Sea. The invasive species are described and the possible ways of introduction of these species with the ships ballast waters are discussed.
V.A. Silkin & I.K. Evstigneeva
PRODUCTIVITY OF TWO MORPHOLOGICAL FORMS OF LAURENCIA PAPILLOSA (FORSK.) GREV. (RHODOPHYTA) IN CULTURE
Productive properties of the Black Sea agar-containing alga Laurencia papillosa (Forsk.) Grev. (Rhodophyta) have been investigated in enrichment culture during 30 days. It was shown that under temperature 15oС and light intensity 40 W/m2 PAR alga had higher specific growth rate. Values of specific growth rate and maximal specific growth rate made up 0.085 and 0.165 day-1 respectively. Two morphological forms of laurencia were tested as concern their reaction on the changes of light intensity and temperature to find correlation between morphostructure of the thallus and its productive characteristics under different conditions of cultivation. The experiment has demonstrated that morphostructure of thalli in the population may determine productive properties of laurencia under nearly optimal conditions.
Jayant Doke, V. Kalyan Raman & V.S. Ghole
TREATMENT OF ANAEROBICALLY DIGESTED WASTEWATER USING SPIRULINA SP.
Spirulina can be cultivated in wastewater to improve water quality. Batch studies were conducted for the treatment of anaerobically digested wastewater (ADW) by using Spirulina sp. This study examines the possibility of using Spirulina sp. to remove COD, BOD, heavy metals, and bacteria from wastewater. The results showed that the growth of Spirulina in ADW was poor, but can be enhanced by the addition of NaHCO3 - up to 4% to 5% as a carbon source, which gives maximum productivity at 1.4 mg/L. It also showed the removal of COD up to 80%, BOD up to 95%, and cations such as potassium 98%, calcium 96%, magnesium 95%, and sodium 90%. Anions such as chloride 51%, nitrate 52%, phosphate 76% and sulphate up to 60% were removed from effluent heavy metals, e.g., Ni was removed up to 57% and Pb up to 97% the total bacterial count was reduced up to 75% in the growth period of eight days.
№3 (2005)
P.V. Yevstigneyev & V.P. Yevstigneyev
SPONTANEOUS BIOLUMINESCENCE OF NOCTILUCA SCINTILLANS SUR. (DINOPHYTA)
The paper is concerned with the spontaneous light emission of Noctiluca scintillans Sur. (Dinophyta) cells in the pure sea water and with the addition of a toxicant. It has been established that frequency of microflashes is a function of cell density and is not associated only with mechanical contacts. The addition of various doses of a toxicant results in low-level oscillating luminescence, the Oscillation period of which depends on the toxicant concentration and time of exposition.
N.A. Mistratova, E.A. Ivanova, V.L. Kolesnikova
ALGOFLORA SOILS IN THE CONDITIONS OF THE COVERED LAND WHICH IS SUBJECTED TO THE INFLUENCE OF THE CHEMICAL FERTILIZER
The species composition of the soil algae growing in the covered land in the Siberian conditions has been studied for the first time. The common trends of algae development under the influence of the chemical fertilizer have also been revealed.
L.A. Shchur, V.N. Lopatin
MODERN SANITARY-ECOLOGICAL STATE OF WATER OF THE UNDERCURRENT THE RIVER ANGARA (KRASNOYARSK REGION, RUSSIA) ON A PHYTOPLANKTON AND MICROPHYTOPERIPHYTON
Qualitative composition of a phytoplankton and microphytoperiphyton of the undercurrent the river Angara for the term July - October 2002 and May - June 2003 represented 184 shecies of algas from 7 division; is most diversiform represented diatomic (83 таксона) and green (54 таксона) to an alga. High degree of complexity and the high values of an index of Shannon Hb (2.00-3.54) were in a phytoplankton in a majority of samples; in a microphytoperiphyton on the majority of samples differed by low values Hb (0.01-1.43). The evaluation of water quality in terms of biomass and saprobicity indexe of a phytoplankton and microphytoperiphyton (rank evaluations) determine 3 classes of satisfactory cleanness, b-mezosaprobicity. The category trophic of water on a biomass of a phytoplankton (0.59±0.09 mg/L) corresponds to the oligotrophic class, oligomezotrophic to the rank; on a biomass of a microphytoperiphyton (48±9.37 mg/10 cm2) – evtrophic to the class, ev-politrophic to the rank.
V.I. Scherbak, O.V. Bondarenko
PHYTOPLANKTON OF THE DNIESTER TRIBUTARIES BY THE EXAMPLE OF THE SERET RIVER AND TERNOPIL WATER RESERVOIR (UKRAINE)
The phytoplankton of the Seret river and the Ternopil water reservoir was represented by 322 infraspecies taxa including those containing the nomenclative species type. The species of Bacillariophyta and Chlorophyta divisions played the leading part in the diversity formation. The seasonal periodicity of the phytoplankton development has been noticed – high values in summer and low in winter. The ecogeographic characteristic of phytoplankton showed that the main bulk of algae in the explored water bodies was formed by cosmopolites; oligohalobes and indifferents (according to halinity); indifferents (according to pH-relation).
O. S. Тarashchuk
SPECIES COMPOSITION OF PHYTOEPIPHYTON ON POTAMOGETON CRISPUS L. IN THE RIVER SECTION OF KANEV RESERVOIR (UKRAINE)
In May and July 2003 species composition of phytoepiphyton on Potamogeton crispus L. at 7 stations in the main channel and the appendage network of the river section of Kanev reservoir was investigated. 80 species, represented by 85 intraspecific taxa, from three divisions, 8 classes, 22 orders, 32 families and 46 genera were found. It was established, that Bacillariophyta was dominating on the number of species, the second place belonged to Chlorophyta, the third – to Cyanophyta. Nevertheless vegetation of Potamogeton crispus was finishing in June, some specimens, that were kept in July, maintained a rich species composition of phytoepiphyton, resembling species composition in May. In the main channel of the river section of Kanev reservoir taxa of diatom algae occupied all the places among dominating orders, families and genera, but in the a ppendage network the taxa of green algae were on the second or third places. From the received data followed, that taxonomic diversity and the floristic spectra of phytoepiphyton depended on the morphometry and a degree of the flowing of a water body. In the main channel of the river section of Kanev reservoir the epiphytic species rіchness of Potamogeton crispus was great enough, but it was some lower, than in the appendage network. In water bodies of the appendage network (Obolon) the epiphytic species composition was richer than in its branches (Desenka). Coefficients of floristic similarity testified, that distribution of species composition of phytoepiphyton of Potamogeton crispus on the stations of Kanev reservoir had mosaic character.
F.P. Tkachenko, V.P. Gerasimiuk
ALGAE OF WATER BODIES OF ELANETSKY STEPPE NATURE RESERVE (UKRAINE)
Paper deals with results of algofloristic study of Elanetsky Steppe Nature Reserve. Dominant group of algal flora turned to be Bacillariophyta (30 genera, 58 species). Chlorophyta represents by 16 genera and 28 species; Cyanophyta – 6 genera, 8 species; Xanthophyta – 3 genera, 3 species and Euglenophyta – 2 genera, 2 species. Most of the studied reservoirs belong to b -mesosaprobe type.
N.P. Massyuk, G.G. Lilitskaya
PHYTOMONADINA OF UKRAINIAN LEFT-BANK POLISSIA
Data about Phytomonadina of Ukrainian Left-Bank Polissia (LBP) water bodies and soils are summarized and filled up. There are known 62 species (64 infraspecific taxa) of Phytomonadina from one class Chlorophyceae, three orders, eight families and 18 genera of Chlorophyta. Among Phytomonadina of LBP Chlamydomonadales (83.9%), Chlamydomonadaceae (75.9%) and Chlamydomonas (53.3%) are dominating taxa on number of species. The annotated list of 19 species Phytomonadina found by autors in water bodies of LBP in 1997-2004 is arranged. Species names are accompanied by original illustrations, nomenclature citations, data about morphological peculiarities of local populations, occurrence, locations, distribution in Ukraine and general distribution. 12 species are new for flora of LBP, 6 – for Ukrainian Polissia, 3 – for Ukraine. One species (Phyllariochloris tenuis Massjuk et Lilits. sp. nov.) is described as new for science (Latin diagnosis, description, illustrations), one is cited as Chlamydomonas sp. (description, illustrations). New locations are pointed out for 7 species. Future investigation of green flagellated algae strategy is discussed.
G.K. Khursevich, S.A. Fedenya
THALASSIOBECKIACEAE – A NEW FAMILY OF THE CLASS CENTROPHYCEAE (BACILLARIOPHYTA)
A new freshwater genus Thalassiobeckia studied in light (LM) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) from the Pliocene sediments of Lake Baikal has been considered in the composition of the new monotype family Thalassiobeckiaceae in the class Centrophyceae (Bacillariophyta). Both new taxa are diagnosed by a combination of following morphological features: a) the presence of loculate areolae with internal cribra and external foramina; b) the arrangement of areolae on the valve face in radiating non-fasciculated striae; c) the presence of the marginal ring of tubular processes on the valve mantle; d) the availability of several rimoportulae on the valve face/mantle junction and e) the availability of one-several valve face fultoportula.
A.F. Krakhmalny, S.P. Wasser, & E. Nevo
NEW SPECIES OF THE GENUS HEMIDINIUM STEIN (DINOPHYTA) FROM ISRAEL
New species Hemidinium nephroideum Krachmalny sp. nov. (Dinophyta) was found in a rain pool in the upper section of Nahal Oren basin, Mount Carmel near Haifa (Israel). H. nephroideum has common features with representatives of genera Hemidinium Stein and Bernardinium Chodat. Due to the theca structure the authors refer the new species to the genus Hemidinium. In the paper we present diagnosis of new species, its comparison with a similar species, H. nasutum Stein, and original drawings and SEM - microphotographs.
R.E. Romanov
THE FINDS OF RARE FOR THE SOUTH OF WEST SIBERIA HETEROTROPHIC ALGAE SPECIES
The facts about rare for West Siberia heterotrophic algae (14 species) of Upper Ob basin mountain and plain rivers and lakes are given. All discovered heterotrophic flagellates were reported earlier from West and East Europe reservoirs.
№4 (2005)
N.A. Davidovich
INHERITANCE OF THE SEX AT THE INTRACLONAL REPRODUCTION OF THE OBLIGATORILY DIOECIOUS SPECIES NITZSCHIA LONGISSIMA (BREB.) RALFS (BACILLARIOPHYTA)
Male clones of the pennate heterothallic diatom Nitzschia longissima (Breb.) Ralfs were studied. Infrequently they are able to intraclonal reproduction. Predicting diplogenotypic mode of sex inheritance we checked the sex of descendants resulting from the intraclonal reproduction. Both male and female viable and fertile clones were revealed in the intraclonal progeny. Male descendants proved to be able to reproduce themselves intraclonally as well. Two new clones derived from the second inbred generation turned to be male ones. The sexual process was isogamous when intraclonal reproduction take place and heterogamous at interclonal reproduction. The gamete form and behavior are heritable attributes associated with the sex. The possibility of change of "monoecious" and "dioecious" generations in the life cycles of diatoms is discussed.
E.I. Shnyukova, Т.I. Мikhailyuk, Т.М. Darienko & S.Ya. Kondratyuk
CONTRIBUTION TO STUDY OF CARBOHYDRATES IN TERRESTRIAL ALGAE
As a result of study of the ratio of various groups of carbohydrates in cells of widely distributed terrestrial algae Desmococcus olivaceus (Pers. ex. Ach.) Laundon, Trentepohlia umbrina (Kutz.). Born., Nostoc commune Vauch., Gloeocapsa magma (Breb.) Kutz. it was revealed that the main part of their carbohydrates are concentrated in the groups of reserve and structural polysaccharides. The fraction of low-polymeric carbohydrates was represented scanty. The comparison of obtained data with information concerning carbohydrates of phylogenetically relative species of aquatic forms has shown that in green algae more than the half of carbohydrates belongs to low - polymeric fraction. In cells of aquatic blue-green algae ratio of carbohydrate groups is similar to those of terrestrial algae. It is supposed that revealed composition of carbohydrates in terrestrial algae helps them in survival in unfavorable environmental conditions; it is related to cell protection against desiccation and supports their vital activity during the period of anabiosis. Similar ratio of carbohydrates in the cells of terrestrial and aquatic blue-green algae, in our opinion, is related to their high plasticity and the ability of a great number of species to inhabit various ecotopes, ranging from water bodies to dry rocks.
V.E. Zaika
THE FEEDING OF MARINE HETEROTROPHIC DINOFLAGELLATE NOCTILUCA SCINTILLANS (MACARTNEY) KOF. ET SWEZY BY CYANOBACTERIA FROM GENUS SYNECHOCOCCUS
Results of microscopic observations and experiments on feeding of the Black Sea Noctilluca scintillans (Macartney) Kof. et Swezy by cyanobacteria are presented. For the comparison flagellate Monochrysis lutheri Droop have been used. During 8 days at 8-10OC in the darkness Noctiluca showed minimal rate of division (25% of the initial number for 8 days) with considerable mortality rate. It is assumed that in winter cyanobacteria can serve as supporting food for N. scintillans.
M.M. Basova
FATTY ACID COMPOSITION OF THE LIPIDS OF CERTAIN SPECIES OF MICROALGAE
The review deals with the analysis of the data available in literature concerning the fatty acid composition of lipids of various species of microalgae depending on conditions of their cultivation. Totally 45 species of marine and brackish water microalgae belonging to 7 classes are recommended for commercial cultivation to obtain polyunsaturated fatty acids and their products, important for medicine and nutrition of humans and animals.
S.I. Genkal, M.S. Kulikovskyi
SPECIES OF GENUS NAVICULA BORY (BACILLARIOPHYTA) IN DIFFERENT TYPE WATER BODIES OF THE NORTH-EAST PART OF PENZA DISTRICT (RUSSIA)
As a result of electron microscopy study of Bacillariophyta of different type water bodies of Penza district, 49 representatives of the genus Navicula were revealed. Among them two species (N. joubaudii Germain and N. saprophila Lange-Bertalot et Bonik.) are new for Russia.
O.V. Gerasymova
RARE SPECIES OF ALGAE FROM THE RESERVOIRS OF DNIPROVSKO-ORILSKY NATURAL RESERVE (UKRAINE)
As result of study of algal flora of Dniprovsko-Orilsky Natural Reserve in 2003-2004 8 rare noteworthy species were found. Among them one species (Uronema elongatum Hodg.) is new for Ukraine, 5 species (Bacularia vermicularis (Fedor.) Kom. et Anagn., Stipitoporos polychloris Ettl,Characium conicum Korsch., Granulocystis helenae Hind., Scenedesmus raciborskii Wolosz.) are the first records for Steppe zone of Ukraine and 2 species (Cosmoastrum teliferum (Ralfs) Pal.-Mordv., Staurastrum tetracerum var. validum W. West et G.S. West) are the second records for Steppe zone of Ukraine.
P.M. Tsarenko
NOMENCLATURE AND TAXONOMIC CHANGES IN THE SYSTEM OF "GREEN" ALGAE
The modern system of "green" algae of Ukraine concordant with morphological, cytological and molecular data is presented. A new family Bracteacoccaceae (Sphaeropleales, Chlorophyceae) is desribed, one more original family Scotiellocystoidaceae (Chlorococcales, Chlorophyceae) is proposed. Some nomenclatural changes at specifies and infraspecies levels are given.
E.N. Demchenko, T.I. Mikhailyuk
NEW SPECIES OF GENUS POLYTOMA EHR. (CHLAMYDOMONADACEAE, CHLOROPHYTA)
Latin diagnosis, description, drawings and microphotographs of new species from the genus Polytoma: P. loricatum Demchenko sp. nov. are presented. The species was found in the summer rain pool in Kiev. Variability of morphological characters of new species and differences from the both known species of this genus and other genera of colorless flagellates are discussed.
O.N. Vinogradova, O.V. Kovalenko
TAXA OF CYANOPHYTA (CYANOPROCARYOTA) NEW FOR UKRAINE
Descriptions and drawings of 10 taxa of blue-green algae first cited for Ukraine are presented, namely of Gloeocapsa compacta Kutz., Chroococcopsis epiphytica Geitler, Xenococcus rivularis (Hansg.) Geitler, Chamaesiphon minimus Schmidle, Chamaesiphon oncobyrsoides Geitler, Cyanophanon mirabile Geitler, Geitleribactron subaequale (Geitler) Komarek, Phormidium subfuscum Kutz. ex Gomont f. inaequale (Nageli) Elenkin, Hydrocoleus muscicola Hansg., Homoeothrix balearica (Bornet et Flahault) Lemmerm. f. tenuis (W. et G.S. West) V. Poljansk.
G.N. Apryshko, M.V. Nekhoroshev, V.N. Ivanov, N.A. Milchakova
ANTITUMOR SUBSTANCES FROM MARINE MACROALGAE OF THE MEDITERRANEAN BASIN
The paper surveys the effect of antitumor substances obtained from the Mediterranean macroalgae on certain cancer diseases in animals. Chemical composition of a number of substances is given; the results of their application are described. The possibility of development in Ukraine of the industry of drug production on the base of marine macroalgae is discussed.

|



